
Archives


Antibiotic Resistance & Bacterial Evolution: What’s the Real Story?
Long Story Short: Episode 3
Darwin’s Impact on Society in Under 3 Minutes
His Ideas Changed Our World
A Whale of an Evolution Tale
Episode Two of Long Story Short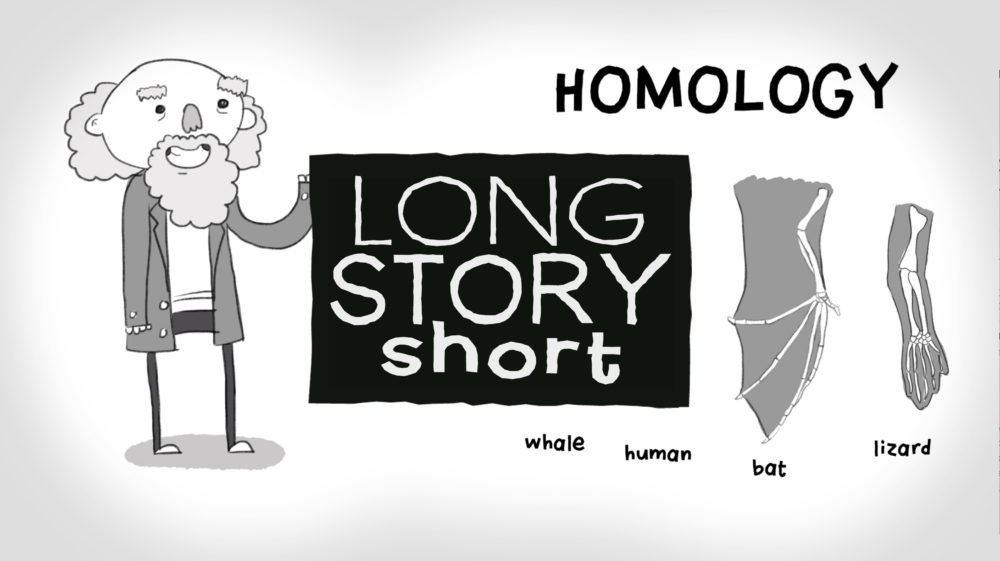
Is Homology Evidence for Evolution?
Long Story Short: Episode 1
Responses to Criticism of Michael Behe’s Darwin Devolves
An evolving record of the scientific dialogue on Darwin Devolves
Scientists Dissent from Darwinian Theory
The Scientist Who Shouldn’t Exist — New Book by Matti Leisola, Jonathan Witt

Essential Readings
Intelligent Design, Darwinian Evolution, and the Impact of Science on Culture
The Workhorse of the Cell: Kinesin

A Précis of Darwin’s Doubt
The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent Design
ATP Synthase: The Power Plant of the Cell

Science and Human Origins
Peer Reviewed Works

Is the Human Genome Garbage?
Biologist says "no" in new book The Myth of Junk DNA
California Science Center to Pay Attorneys’ Fees and Settle Open Records Lawsuit by Intelligent Design Group

What Is Evolution?

What Is the Science Behind Intelligent Design?

Design in the Bible and the Early Church Fathers

The Design of Life: Discovering Signs of Intelligence In Biological Systems
For the newcomer to ID, Design of Life offers clearly written and well-illustrated chapters explicating ID's basic scientific concepts, such as irreducible complexity and specified complexity. Design of Life even gives accessible discussions of more complex issues, such as the "irreducible core," or explaining how specified complexity is detected in the research of Douglas Axe, who found that the odds of obtaining a functional β-lactamase domain are less than one in 10^64.
For the ID-guru, Design of Life covers many hot topics. This includes a lucid explanation of the integrated, unevolvable complexity in the neck of the giraffe, a potent critique of the alleged transition from reptiles to mammals, and a critical analysis of the evidence used to support the hypothesis that whales evolved from land-mammals. The advanced reader will devour the General Notes, which expose the bankruptcy of Darwinist attacks...