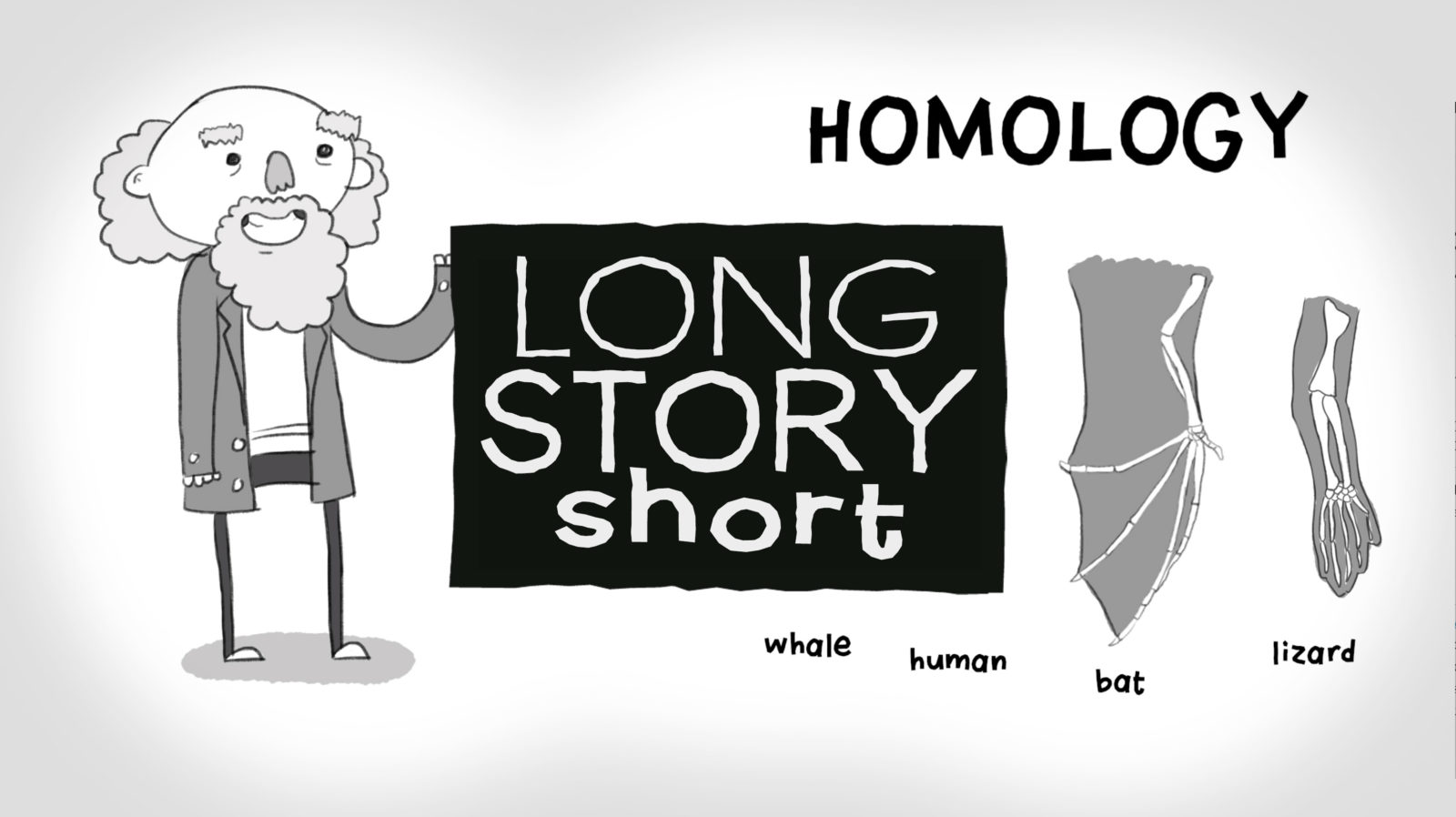
Is Homology Evidence for Evolution?
Is homology due to common descent or common design? Is descent with modification overwhelmingly obvious? The standard definition of homology is the similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a common evolutionary ancestor- the structural identity of parts in distinct species such as the human hand, the wing of a Read More ›




